I already mentioned that there is another type of pressure called gaseous pressure which is studied in the special branch in chemistry which has been developed from 18th century onwardscalled gaseous states,. which completely deals on the pressure , temperature, volume,and number of atoms in the gaseous mixtures or one single type of gas,.there are number of laws and theories in this branch like boyles law,charles law ,avagadros law,gaylussac law,grahams law,daltons law,ideal gas equations,.
boyles law:pressure(p) is inversely proportional to volume(v) at a fixed temparature(T).
charles law: volume(v) is directly proportional to temperature(T) at a fixed pressure(p).
gaylussacs law: pressure(p) is directly proportional to temperature(T) at constant volume(v).
avagadros law: volume(v) occupied by ideal gas is proportional to number of molecules of the gas in that container(n).
grahams law: rate of diffusion of a gas is inversly proportional to square root of density(d).
daltons law: the pressure of the total gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of pressures of individual components of the gases in the mixture.and this law is also called as the daltons law of partial pressures.
henrys law:At constant temperature, the amount of a given gas dissolved in a
given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid.
ideal gas equation: the combinations of all the above gas laws gives the ideal gas equation whic is PV=nRT.
and even some more information can be gathered in further posts.keep going with our favorite bloggers of science.......(supersscience.blogspot.com)........




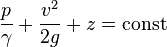
 = pressure head
= pressure head = velocity head
= velocity head



 .
.