In this blog we are going to have the brief glance on the Fluid pressure.which combine the liquid and gaseous pressures.in this blog lets have liquid pressure.
Closed bodies of fluid are either "static", when the fluid is not moving, or "dynamic", when the fluid can move as in either a pipe or by compressing an air gap in a closed container. The pressure in closed conditions conforms with the principles of fluid dynamics
The concepts of fluid pressure are predominantly attributed to the discoveries of blaise pascle and daniel bernoulli.bernoullie equation can be used in almost any situation to determine the pressure at any point in a fluid. The equation makes some assumptions about the fluid, such as the fluid being ideal and incompressible.An ideal fluid is a fluid in which there is no friction, it is inviscid,zero viscosity. The equation for all points of a system filled with a constant-density fluid is
where:
Fluid pressure is the pressure at some point within a fluid such as water or air. Fluid pressure occurs in one of two situations:
- an open condition, called "open channel flow", e.g. the ocean, a swimming pool, or the atmosphere.
- a closed condition, called "closed conduit", e.g. a water line or gas line.
Closed bodies of fluid are either "static", when the fluid is not moving, or "dynamic", when the fluid can move as in either a pipe or by compressing an air gap in a closed container. The pressure in closed conditions conforms with the principles of fluid dynamics
The concepts of fluid pressure are predominantly attributed to the discoveries of blaise pascle and daniel bernoulli.bernoullie equation can be used in almost any situation to determine the pressure at any point in a fluid. The equation makes some assumptions about the fluid, such as the fluid being ideal and incompressible.An ideal fluid is a fluid in which there is no friction, it is inviscid,zero viscosity. The equation for all points of a system filled with a constant-density fluid is
where:
- p = pressure of the fluid
- γ = ρg = density·acceleration of gravity = specific gravity of the fluid.
- v = velocity of the fluid
- g = acceleration due to gravity
- z = elevation
 = pressure head
= pressure head = velocity head
= velocity head
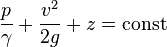
No comments:
Post a Comment