- In this session i am going to explain the topics noted in the previous post
- Dry friction resists relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into static friction ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and kinetic friction between moving surfaces.
- Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other.
- Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricate fluid separates two solid surfaces.
- Skin friction is a component of drag the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body.
- Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a solid material while it undergoes deformation.
- Friction is not itself a fundemental force Dry friction arises from a combination of inter-surface adhesion, surface roughness, surface deformation, and surface contamination.
- The elementary property of sliding (kinetic) friction were discovered by experiment in the 15th to 18th centuries and were expressed as three empirical laws:
- Amontons first law: The force of friction is directly proportional to the applied load.
- Amontons' Second Law: The force of friction is independent of the apparent area of contact.
- Coulomb's Law of Friction: Kinetic friction is independent of the sliding velocity.
- Static friction:Static friction is friction between two or more solid objects that are not moving relative to each other. For example, static friction can prevent an object from sliding down a sloped surface. The coefficient of static friction, typically denoted as μs, is usually higher than the coefficient of kinetic friction.The maximum value of static friction, when motion is impending, is sometimes referred to as limiting friction, although this term is not used universally. It is also known as traction.
- it can be overcomes through the reverse force applied in the path of the moving object.
- An example of static friction is the force that prevents a car wheel from slipping as it rolls on the ground. Even though the wheel is in motion, the patch of the tire in contact with the ground is stationary relative to the ground, so it is static rather than kinetic friction.
- Khinetic friction:Kinetic (or dynamic) friction occurs when two objects are moving
relative to each other and rub together (like a sled on the ground). The
coefficient of kinetic friction is typically denoted as μk, and is usually less than the coefficient of static friction for the same materials. However, richard feynman comments that "with dry metals it is very hard to show any difference."
The friction force between two surfaces after sliding begins is the
product of the coefficient of kinetic friction and the normal force:
 .
. - Fluid friction: Fluid friction occurs between layers within a fluid that are moving relative to each other. This internal resistance to flow is described as viscosity.
In everyday terms viscosity of a fluid is said to have "thickness".
Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick",
having a higher viscosity. The less viscous the fluid, the greater its
ease of movement.
All real fluids (except super fluids) have some resistance to stress and therefore are viscous, but a fluid which has no resistance to shear stress is known as an ideal fluids or inviscid fluid.
lubrication friction: Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a fluid separates two solid surfaces. Lubrication is a technique employed to reduce wear of one or both surfaces in close proximity moving relative to each another by interposing a substance called a lubricant between the surfaces.
skin friction: Skin friction arises from the friction of the fluid against the "skin" of the object that is moving through it. Skin friction arises from the interaction between the fluid and the skin of the body, and is directly related to the area of the surface of the body that is in contact with the fluid. Skin friction follows the drag equationand rises with the square of the velocity.
Skin friction is caused by viscous drag in the boundary layers around the object. There are two ways to decrease skin friction: the first is to shape the moving body so that smooth flow is possible, like an airfoil. The second method is to decrease the length and cross-section of the moving object as much as is practicable.
Internal friction:Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a solid material while it undergoes deformation.
plastic deformation in solids is an irreversible change in the internal molecular structure of an object. This change may be due to either (or both) an applied force or a change in temperature. The change of an object's shape is called strain. The force causing it is called stress
Elastic deformation in solids is reversible change in the internal molecular structure of an object. Stress does not necessarily cause permanent change. As deformation occurs, internal forces oppose the applied force. If the applied stress is not too large these opposing forces may completely resist the applied force, allowing the object to assume a new equilibrium state and to return to its original shape when the force is removed. This is known as elastic deformation or elasticity.
Rolling resistance is the force that resists the rolling of a wheel or other circular object along a surface caused by deformations in the object and/or surface. Generally the force of rolling resistance is less than that associated with kinetic friction. Typical values for the coefficient of rolling resistance are 0.001.One of the most common examples of rolling resistance is the movement of motor vehicle tires on a road, a process which generates heat and sound as by-products.
triboelectric effect:Rubbing dissimilar materials against one another can cause a build-up of electrostatic charge which can be hazardous if flammable gases or vapors are present. When the static build-up discharges, explosions can be caused by ignition of the flammable mixture.
belt friction: Belt friction is a physical property observed from the forces acting on a belt wrapped around a pulley, when one end is being pulled. The resulting tension, which acts on both ends of the belt, can be modeled by the belt friction equation.
In practice, the theoretical tension acting on the belt or rope calculated by the belt friction equation can be compared to the maximum tension the belt can support. This helps a designer of such a rig to know how many times the belt or rope must be wrapped around the pulley to prevent it from slipping. Mountain climbers and sailing crews demonstrate a standard knowledge of belt friction when accomplishing basic tasks.
some other important topics related friction can be learned in the further posts of superscience.blogspot.com keep going with this blog......................
Monday, 31 August 2015
Saturday, 29 August 2015
In this session we are going to deal on the special type of force called frictional force which is defined as the resistance tat one surface or object that encounters while moving on the other .there are several types of friction they are 1.dry friction,2.fluid friction 3.lubricated friction.
4.skin friction and 5.internal friction.there are even some other types of frictions such as rolling friction,triboelectric friction, belt friction,there are some more types of frictions which are the sub divisions of the dry friction they are static friction,khinetic friction and all the other imp topics are going to discuss in next blog
4.skin friction and 5.internal friction.there are even some other types of frictions such as rolling friction,triboelectric friction, belt friction,there are some more types of frictions which are the sub divisions of the dry friction they are static friction,khinetic friction and all the other imp topics are going to discuss in next blog
Friday, 28 August 2015
In this session we are going to deal a special type of force called friction....friction is the special type of force which is defined as the resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over the other.
The causes of the restive force of friction are molecular adhesion, surface roughness, and the plowing effect. Adhesion is the molecular force resulting when two materials are brought into close contact with each other. Trying to slide objects against each other requires breaking these adhesive bonds.
The causes of the restive force of friction are molecular adhesion, surface roughness, and the plowing effect. Adhesion is the molecular force resulting when two materials are brought into close contact with each other. Trying to slide objects against each other requires breaking these adhesive bonds.
Thursday, 27 August 2015
In this session we are going to deal with the applications of the magnets and artificial magnets..
there are end number of applications now a days based on the magnets.with out these magnets there will be the lose of some millions of projects which are in process now a days...
some of the applications,uses and projects based on the magnets.....they are.
1.they are used in making the electric motors and generators which converts the electrical energy to mechanical energy vice versa..
2.they are used in the speakers which converts electrical energy to sound energy.
3.used in electrical bells.
4.They are used in the Maglev trains. In the Maglev trains, the super conducting magnets are used on the tracks on which the train floats. These types of the trains are working on the repulsion force of the magnets.
5.They are also used to sort out the magnetic and non magnetic substances from the scrap.
6.They are used in TV screens, computer screens, telephones and in tape recorders.
7.They are used by the candy or cold drink vendors to separate the metallic cap from the lots.
8.They are used in cranes.
9.They are used in the refrigerators to keep the door close.
10.The most important use of the magnet is the magnetic compass which is used to find the geographical directions.
The use of the magnets in the medical sciences is very affective. We can use magnet therapy for the pain management without any use of the medicines. The magnets can stimulate the nerves in the human body and increase the blood circulation, which carries oxygen to the tissues. The magnet are used to heal the pains and the wounds of the athletes. Doctors uses the magnets to cure arthritis, gout, spondilitis and other problems related to the nervous system. Magnetic mattress are used for relaxing the body. In MRI we use the magnets. Magnets are used to cure the depression, headaches and migraines.
these are some general applications of the magnets in the daily life and some other simple workouts with which the magnets are widely using can be listened through the video clip
These are the simple techniques used in the heavy projects like electric power generators,trains and application and so on there are end number of application of magnets and these are the magnetic applications such as magnetic levitation and some others projects whic are going to implement further.....some other important topics can be learned through this blog keep going further................
there are end number of applications now a days based on the magnets.with out these magnets there will be the lose of some millions of projects which are in process now a days...
some of the applications,uses and projects based on the magnets.....they are.
1.they are used in making the electric motors and generators which converts the electrical energy to mechanical energy vice versa..
2.they are used in the speakers which converts electrical energy to sound energy.
3.used in electrical bells.
4.They are used in the Maglev trains. In the Maglev trains, the super conducting magnets are used on the tracks on which the train floats. These types of the trains are working on the repulsion force of the magnets.
5.They are also used to sort out the magnetic and non magnetic substances from the scrap.
6.They are used in TV screens, computer screens, telephones and in tape recorders.
7.They are used by the candy or cold drink vendors to separate the metallic cap from the lots.
8.They are used in cranes.
9.They are used in the refrigerators to keep the door close.
10.The most important use of the magnet is the magnetic compass which is used to find the geographical directions.
The use of the magnets in the medical sciences is very affective. We can use magnet therapy for the pain management without any use of the medicines. The magnets can stimulate the nerves in the human body and increase the blood circulation, which carries oxygen to the tissues. The magnet are used to heal the pains and the wounds of the athletes. Doctors uses the magnets to cure arthritis, gout, spondilitis and other problems related to the nervous system. Magnetic mattress are used for relaxing the body. In MRI we use the magnets. Magnets are used to cure the depression, headaches and migraines.
these are some general applications of the magnets in the daily life and some other simple workouts with which the magnets are widely using can be listened through the video clip
These are the simple techniques used in the heavy projects like electric power generators,trains and application and so on there are end number of application of magnets and these are the magnetic applications such as magnetic levitation and some others projects whic are going to implement further.....some other important topics can be learned through this blog keep going further................
Wednesday, 26 August 2015
In this session we are going to deal with the another types of magnets they are
1.natural (permanent magnets ) and 2. artificial magnets (temporary magnets).
1. Natural magnets: these are the naturally occurring magnets from the earths core,mantle in the form of ores of some metals like iron,cobalt,nickel,and some other rare earth metals like gadolinium,dysprosium etc...
methods to demagnetize a magnet whether it is a temporary or permanent are 1.heating
2.rough handeling 3. by induction 4.and by passing electricity these are the methods to be followed to de magnetize a magnet..
2. Artificial magnets:these are the magnets which are prepared by using natural magnets or without ,which can attract the magnetic material...these magnets can be prepared by some methods they are 1.single touch method.2.double touch method 3.by using electricity to the materials..
1.single touch method: in this method the material going to be magnetized is need to be rubbed by the magnet in the one direction in order to bring the dipoles in the position to attract the other materials...in this method the magnetising material need to be rubbed with a natural permanent magnets..
2.double touch method: in this method the material need to be magnetized in such a way that from the middle of the material to the ends with two different magnets which are need to be placed with the opposite poles.
3.Electromagnets: in this method appropriate material is choosed and it is magnetized by the usage of current in such a way that for a electrical vector there exists a magnetic vector perpendicular to it..
all these methods produces the temporary magnets only but not the permanent....
properties of a magnet: there are six propeties of a magnet they are
1.it attracts magnetic substances
2.it points north-south direction when suspended freely
3.repulsion is sure test for magnetisation
4.poles of the magnets are always paired there donot exists a mono pole in magnets
5.similar poles of magnets repel each other
6.magnetic force can eaisly passes through non magnetic materials...
all the artificial magnets satisifies these propeties for a short time where as the permenant magnets shows the through out they exist,.
some other topics can be learned through supersscience.blogspot.com.....keep going with this blog...........
1.natural (permanent magnets ) and 2. artificial magnets (temporary magnets).
1. Natural magnets: these are the naturally occurring magnets from the earths core,mantle in the form of ores of some metals like iron,cobalt,nickel,and some other rare earth metals like gadolinium,dysprosium etc...
methods to demagnetize a magnet whether it is a temporary or permanent are 1.heating
2.rough handeling 3. by induction 4.and by passing electricity these are the methods to be followed to de magnetize a magnet..
2. Artificial magnets:these are the magnets which are prepared by using natural magnets or without ,which can attract the magnetic material...these magnets can be prepared by some methods they are 1.single touch method.2.double touch method 3.by using electricity to the materials..
1.single touch method: in this method the material going to be magnetized is need to be rubbed by the magnet in the one direction in order to bring the dipoles in the position to attract the other materials...in this method the magnetising material need to be rubbed with a natural permanent magnets..
2.double touch method: in this method the material need to be magnetized in such a way that from the middle of the material to the ends with two different magnets which are need to be placed with the opposite poles.
3.Electromagnets: in this method appropriate material is choosed and it is magnetized by the usage of current in such a way that for a electrical vector there exists a magnetic vector perpendicular to it..
all these methods produces the temporary magnets only but not the permanent....
1.it attracts magnetic substances
2.it points north-south direction when suspended freely
3.repulsion is sure test for magnetisation
4.poles of the magnets are always paired there donot exists a mono pole in magnets
5.similar poles of magnets repel each other
6.magnetic force can eaisly passes through non magnetic materials...
all the artificial magnets satisifies these propeties for a short time where as the permenant magnets shows the through out they exist,.
some other topics can be learned through supersscience.blogspot.com.....keep going with this blog...........
Tuesday, 25 August 2015
In this session we are going to have the discussions on the magnetic material and their types...
what are magnetic materials ?
the material which are attracted by the magnets or made to attract by the magnets are called the magnetic materials . Based on the attraction power of the materials the magnetic materials are divided into 6 types they are 1.Dia magnetic substances .
2.Para magnetic substances.
3.Ferro magnetic substances.
4.Anti ferro magnetic substances.
5.and ferri magnetic substances.
6.superpara magnetic substances.
these are the five types of the magnetic materials which ever we come across in the day to day life... Lets have the detailed information about the magnetic substances.
1.Dia magnetic substances:Dia magnetism is the property of an object which causes it to create the magnetic field in the opposite direction to the applied external magnetic field thus causing the repulsive force.. Dia magnets are the materials with magnetic permiability less than one.the suseptibility is also less than zero i.e., negative.
these materials are independant of the temperature.and do not allows any external field lines through it...
examples are gold,copper,silver etc....
2.Para magnetic substances: these materials are feebly attracted by the external magnetic field and they magnetize in the direction of applied external magnetic field
these material have permanent atomic magnetic dipoles oriented in different directions such thatnet magnetic moment is zero in the absence of external magnetic field...the susceptibility is small and positive and is inversely proportional to the temperature and relative permiability is greater than one
examples aluminium,platinum etc
3.Ferro magnetic substances:These materials are strongly attracted by the magnetic field and they magnetize in the direction of external magnetic field.these materials have the domains.all the dipoles in the same domain align in the same direction and that is different in the adjacent domain so the net magnetic moment is 0. and in the external field all domains gets tuned to the direction of the magnetic field applied.for these materials suseptibility is always high and positive and is dependent on the temperature
examples are iron,cobalt etc.
4.Antiferro magnetic substances : the magnetic dipole moments of the adjacent atoms are anti parallel.due to this anti parallel moments the magnetic moment is 0....generally anti ferro magnetic moments exists at the low temperatures and vanishes at high temperatures called as Neel temperature .for these materials susceptibility is small and positive dependent on temperature
examples are copper chloride,oxides of manganese,etc
5.Ferri magnetic materials: for these materials the dipole moment of adjacent magnetic materials is anti parallel and with different magnitudes.susceptibility is very large and positive and is inversely proportional to temperature.
examples are all ferrites.with divalent atoms of copper xinc etc...
6.superpara magnetic materials : When a ferromagnet or ferrimagnet is sufficiently small, it acts like a single magnetic spin that is subject to brownien motion Its response to a magnetic field is qualitatively similar to the response of a paramagnet, but much larger.
some other types of magnetisms are meta magnetism,molecule based magnetism,spin glass magnetim.
meta magnetism is a sudden (often, dramatic) increase in the magnetisationof a material with a small change in an externally applied magnetic field The metamagnetic behavior may have quite different physical causes for different types of metamagnets. Some examples of physical mechanisms leading to metamagnetic behavior are:
molecule based magnets: Molecule-based magnets are a class of materials capable of displaying ferro magnetism. This class expands the materials properties typically associated with magnets to include low density, transparency, electrical insulation, and low-temperature fabrication, as well as combine magnetic ordering with other properties such as photoresponsiveness. Essentially all of the common magnetic phenomena associated with conventional transition-metal and rare-earth-based magnets can be found in molecule-based magnets
spin glass magnetism A spin glass is a disordered magnet where the magnetic spin of the component atoms (the orientation of the north and south magnetic poles in three-dimensional space) are not aligned in a regular pattern. The term "glass" comes from an analogy between the magnetic disorder in a spin glass and the positional disorder of a conventional, chemical glass e.g., a window glass. In window glass or any amorphous solid the atomic bond structure is highly irregular; in contrast, a crystal has a uniform pattern of atomic bonds. In ferro magnets solid, magnetic spins all align in the same direction; this would be analogous to a crystal.
and in this way magnets are classified based on the attractions. some other intresting topics can be learned from superscience.blogspot.com..........
what are magnetic materials ?
the material which are attracted by the magnets or made to attract by the magnets are called the magnetic materials . Based on the attraction power of the materials the magnetic materials are divided into 6 types they are 1.Dia magnetic substances .
2.Para magnetic substances.
3.Ferro magnetic substances.
4.Anti ferro magnetic substances.
5.and ferri magnetic substances.
6.superpara magnetic substances.
these are the five types of the magnetic materials which ever we come across in the day to day life... Lets have the detailed information about the magnetic substances.
1.Dia magnetic substances:Dia magnetism is the property of an object which causes it to create the magnetic field in the opposite direction to the applied external magnetic field thus causing the repulsive force.. Dia magnets are the materials with magnetic permiability less than one.the suseptibility is also less than zero i.e., negative.
these materials are independant of the temperature.and do not allows any external field lines through it...
examples are gold,copper,silver etc....
2.Para magnetic substances: these materials are feebly attracted by the external magnetic field and they magnetize in the direction of applied external magnetic field
these material have permanent atomic magnetic dipoles oriented in different directions such thatnet magnetic moment is zero in the absence of external magnetic field...the susceptibility is small and positive and is inversely proportional to the temperature and relative permiability is greater than one
examples aluminium,platinum etc
3.Ferro magnetic substances:These materials are strongly attracted by the magnetic field and they magnetize in the direction of external magnetic field.these materials have the domains.all the dipoles in the same domain align in the same direction and that is different in the adjacent domain so the net magnetic moment is 0. and in the external field all domains gets tuned to the direction of the magnetic field applied.for these materials suseptibility is always high and positive and is dependent on the temperature
examples are iron,cobalt etc.
examples are copper chloride,oxides of manganese,etc
5.Ferri magnetic materials: for these materials the dipole moment of adjacent magnetic materials is anti parallel and with different magnitudes.susceptibility is very large and positive and is inversely proportional to temperature.
examples are all ferrites.with divalent atoms of copper xinc etc...
6.superpara magnetic materials : When a ferromagnet or ferrimagnet is sufficiently small, it acts like a single magnetic spin that is subject to brownien motion Its response to a magnetic field is qualitatively similar to the response of a paramagnet, but much larger.
some other types of magnetisms are meta magnetism,molecule based magnetism,spin glass magnetim.
meta magnetism is a sudden (often, dramatic) increase in the magnetisationof a material with a small change in an externally applied magnetic field The metamagnetic behavior may have quite different physical causes for different types of metamagnets. Some examples of physical mechanisms leading to metamagnetic behavior are:
- Itinerant Metamagnetism - exchange splittingof the fermi surface in a para magnetic system of itinerant electrons causes an energetically favorable transition to bulk magnetization near the transition to a ferro magnet or other magnetically ordered state.
- Antiferromagnetic Transition - Field-induced spin flips in anti ferro magnets cascade at a critical energy determined by the applied magnetic field.
molecule based magnets: Molecule-based magnets are a class of materials capable of displaying ferro magnetism. This class expands the materials properties typically associated with magnets to include low density, transparency, electrical insulation, and low-temperature fabrication, as well as combine magnetic ordering with other properties such as photoresponsiveness. Essentially all of the common magnetic phenomena associated with conventional transition-metal and rare-earth-based magnets can be found in molecule-based magnets
spin glass magnetism A spin glass is a disordered magnet where the magnetic spin of the component atoms (the orientation of the north and south magnetic poles in three-dimensional space) are not aligned in a regular pattern. The term "glass" comes from an analogy between the magnetic disorder in a spin glass and the positional disorder of a conventional, chemical glass e.g., a window glass. In window glass or any amorphous solid the atomic bond structure is highly irregular; in contrast, a crystal has a uniform pattern of atomic bonds. In ferro magnets solid, magnetic spins all align in the same direction; this would be analogous to a crystal.
and in this way magnets are classified based on the attractions. some other intresting topics can be learned from superscience.blogspot.com..........
Saturday, 22 August 2015
In this session i need to discuss on the magnets,magnetic forces, magnetic fields and its uses..
what about magnets to know,lets have the explanation....
history about magnets......
the first discussion on the magnetism was done by Thales of milieus and at the same time an Indian great doctor,surgeon,scientist susrutha used for the first time the magnets in a surgical process in around 625bc and the first magnetic compass was discovered by the Chinese based on the lodestone which is a natural occurring magnets in the earth.
how the lodestone gets magnetized is a very meritorious thing up to now since the earths weak magnetic field is not enough to magnetize the ores inside the earth......
how this earth even gets the magnetic power?
in the previous session about the gravity i discussed that the gravity produces the attraction which in other words is a type of magnetic force due to spin.
how the magnetic force is included in any bodies is mainly based on the two ways spin and orbital motions of the atoms inside it which forms the dipoles of magnets and the other is electrical forces
(gravity produces magnetic power and it produces the electric power)( vice versa )
there is so much to discuss about the magnetism which is the infinitely using knowledge now a days...that is:
1.magnetic materials .
2.magnetic fields
3. types of magnetic materials.
4.artificial magnets
5.projects based on the magnetism
one by one i will discuss in the further posts....keep going with supersscience.blogspot.com
what about magnets to know,lets have the explanation....
history about magnets......
the first discussion on the magnetism was done by Thales of milieus and at the same time an Indian great doctor,surgeon,scientist susrutha used for the first time the magnets in a surgical process in around 625bc and the first magnetic compass was discovered by the Chinese based on the lodestone which is a natural occurring magnets in the earth.
how the lodestone gets magnetized is a very meritorious thing up to now since the earths weak magnetic field is not enough to magnetize the ores inside the earth......
how this earth even gets the magnetic power?
in the previous session about the gravity i discussed that the gravity produces the attraction which in other words is a type of magnetic force due to spin.
how the magnetic force is included in any bodies is mainly based on the two ways spin and orbital motions of the atoms inside it which forms the dipoles of magnets and the other is electrical forces
(gravity produces magnetic power and it produces the electric power)( vice versa )
there is so much to discuss about the magnetism which is the infinitely using knowledge now a days...that is:
1.magnetic materials .
2.magnetic fields
3. types of magnetic materials.
4.artificial magnets
5.projects based on the magnetism
one by one i will discuss in the further posts....keep going with supersscience.blogspot.com
Thursday, 20 August 2015
In the previous sessions we discussed about gravity and its applications in this session we need to discuss about the stellar energy......!
How stars get energy to illuminate the energy?
how they are emitting heat and light from thousands and millions of years together?
lets have a detailed history about this concept....
This observations and researches were started in mid 1800's.......
In the mid 1800;s two physicists lord kelvin and Hermann von helmholtz,put forward the idea that the huge weights of sun's outer layers should cause the sun to gradually contract.as it does so the gases in its interior becomes compressed and when a gas is compressed its temperature increases...and these two scientists argued that gravitational contraction would cause the suns gases to become hot enough to radiate heat energy into space.This process called kelvin-Helmholtz contraction,does infact happen in the protostar phase of stellar formation.....
But after them in 1920 Aurthur Eddington proposed that stars obtain their energy from nuclear fusion of hydrogen to form helium and raised the possibility that the heavier elements are produced in stars.this was the preliminary step towards the idea of nucleosynthesis in 1928.....
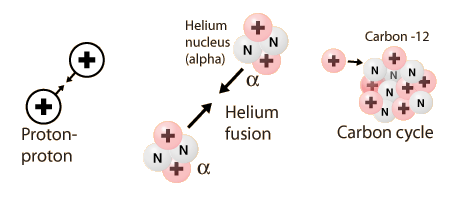
And in 1939,hans bethe analyzed different possibilities of analyzed the different possibilities for reactions by which hydrogen is fused into helium. He defined two processes that he believed to be the sources of energy in stars.they are1.proton-proton chain reaction and
2.carbon-nitrogen cycle.which are the two main energy sources for the stars..
1.proton proton cycle:
this cycle consist of three steps in which hydrogen is converted to helium

And the next proecss is carbon-nitrogen cycle(or)cno cycle:






In the way the two processes continues till the all available atoms completely gets converted to Helium or the energy (heat and light or even radiation )
.And we may have to consider the newly emerged theories by which stellar energy is produce are given as follows...................
- Hydrogen fusing:
- Helium burning:
- The triple-alpha process
- The alpha process
- Burning of heavier elements:
- Lithium burning: a process found most commonly in brown dwarfs
- Carbon burning process
- Neon burning process
- Oxygen burning process
- Silicon burning process
- Production of elements heavier than iron:
- Neutron capture:
- Proton capture:
- The Rp-process
- Photo-disintegration:
- The P-process
Tuesday, 18 August 2015
some other relevant topics based on the gravitational force are given below
- Angular momentum
- Anti-gravity, the idea of neutralizing or repelling gravity
- Artificial gravity
- Birkeland current
- Gravitational wave
- Gravitational wave background
- Cosmic gravitational wave background
- Einstein–Infeld–Hoffmann equations
- Escape velocity, the minimum velocity needed to escape from a gravity well
- g-force, a measure of acceleration
- Gauge gravitation theory
- Gauss's law for gravity
- Gravitational binding energy
- Gravity assist
- Gravity gradiometry
- Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment
- Gravity Research Foundation
- Jovian–Plutonian gravitational effect
- Kepler's third law of planetary motion
- Lagrangian point
- Micro-g environment, also called microgravity
- Mixmaster dynamics
- n-body problem
- Newton's laws of motion
- Pioneer anomaly
- Scalar theories of gravitation
- Speed of gravity
- Standard gravitational parameter
- Standard gravity
- Weightlessness
- all these are available in the Wikipedia of gravity you can have the detailed explanition for each and every topic in the post available to you now....
theories proposed based on the gravitational force..
- Aristotelian theory of gravity
- Le Sage's theory of gravitation (1784) also called LeSage gravity, proposed by Georges-Louis Le Sage, based on a fluid-based explanation where a light gas fills the entire universe.
- Ritz's theory of gravitation, Ann. Chem. Phys. 13, 145, (1908) pp. 267–271, Weber-Gauss electrodynamics applied to gravitation. Classical advancement of perihelia.
- Nordström's theory of gravitation (1912, 1913), an early competitor of general relativity.
- Kaluza Klein theory (1921)
- Whitehead's theory of gravitation (1922), another early competitor of general relativity.
- Brans–Dicke theory of gravity (1961) [33]
- Induced gravity (1967), a proposal by Andrei Sakharov according to which general relativity might arise from quantum field theories of matter
- ƒ(R) gravity (1970)
- Horndeski theory (1974) [34]
- Supergravity (1976)
- String theory
- In the modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) (1981), Mordehai Milgrom proposes a modification of Newton's Second Law of motion for small accelerations [35]
- The self-creation cosmology theory of gravity (1982) by G.A. Barber in which the Brans-Dicke theory is modified to allow mass creation
- Loop quantum gravity (1988) by Carlo Rovelli, Lee Smolin, and Abhay Ashtekar
- Nonsymmetric gravitational theory (NGT) (1994) by John Moffat
- Tensor–vector–scalar gravity (TeVeS) (2004), a relativistic modification of MOND by Jacob Bekenstein
- Gravity as an entropic force, gravity arising as an emergent phenomenon from the thermodynamic concept of entropy.
- In the superfluid vacuum theory the gravity and curved space-time arise as a collective excitation mode of non-relativistic background superfluid.
- Chameleon theory (2004) by Justin Khoury and Amanda Weltman.
- Pressuron theory (2013) by Olivier Minazzoli and Aurélien Hees.
Monday, 17 August 2015
can we over come the gravitational force?
Its highly difficult to over come the gravitational force even in the space also.since if we go to the moon there exists the attractions of earth,sun and if we go beyond the solar system there exists the attractions of milky way galaxies and if we go beyond this milky way galaxy there exists Andromeda galaxies attraction and this continues up to the nebules,clusters clustergroups,massive stars etc.....there fore we cannot overcome the gravity at any section in universe but up to some extent we can.. over come the gravity on earth itself!
How? By the 1.huge rotation(centrifuge process(or)gyroscopic persession) and
By 2.heavy reaction towards the earth(according to newton's third law:for every action there is equal and opposite reaction)
by the usage of the two forces we can over come the gravitational forces on earth itself ...
we cannot lift that one with out rotation because of gravity.but we can by gyroscopic persession .and this video gives that how we can overcome the gravity by centrifuge(heavy rotation)...and the second repelling force of gravity is given through the example of rockets...
In which the fuel in the rockets hits the ground with a high speed which gives the reaction to the rocket which should move upwards with a high speed of 11.2 km/s..at this high reaction towards earth leads the rocket into the space.
so we can clearly say that we can overcome the gravity upto some extent only.....
The other super science topics can be learned through supersscience.blogspot.com keep going with this blog........
Its highly difficult to over come the gravitational force even in the space also.since if we go to the moon there exists the attractions of earth,sun and if we go beyond the solar system there exists the attractions of milky way galaxies and if we go beyond this milky way galaxy there exists Andromeda galaxies attraction and this continues up to the nebules,clusters clustergroups,massive stars etc.....there fore we cannot overcome the gravity at any section in universe but up to some extent we can.. over come the gravity on earth itself!
How? By the 1.huge rotation(centrifuge process(or)gyroscopic persession) and
By 2.heavy reaction towards the earth(according to newton's third law:for every action there is equal and opposite reaction)
by the usage of the two forces we can over come the gravitational forces on earth itself ...
In which the fuel in the rockets hits the ground with a high speed which gives the reaction to the rocket which should move upwards with a high speed of 11.2 km/s..at this high reaction towards earth leads the rocket into the space.
so we can clearly say that we can overcome the gravity upto some extent only.....
The other super science topics can be learned through supersscience.blogspot.com keep going with this blog........
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)