In this session we are going to deal on the further topics of fluid pressure...
By observing all the propeties of pressure in liquids pascle proposed the law to say the directions of pressure applying in the liquid and its molecules .the below video states the law produced by him and its applications....
even there are so many laws related to the fluid pressure like bernoullis law etc
even more types of pressures are known now a days some of them are stagnation pressure,
surface pressure,buoyant pressure,kinematic pressure,dynamic pressure and static pressures.and there is an other topic which is a special type comes under the gaseous pressure which is another special topic dealed in further posts...
By observing all the propeties of pressure in liquids pascle proposed the law to say the directions of pressure applying in the liquid and its molecules .the below video states the law produced by him and its applications....
even more types of pressures are known now a days some of them are stagnation pressure,
surface pressure,buoyant pressure,kinematic pressure,dynamic pressure and static pressures.and there is an other topic which is a special type comes under the gaseous pressure which is another special topic dealed in further posts...
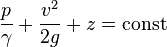
 = pressure head
= pressure head = velocity head
= velocity head

